The Only Guide to Lumbar Spine Surgery & Anatomy Lone Tree - Bradley Duhon


Spinal Osteoarthritis Symptoms
Everything about A Comparative Analysis of X-ray Findings of the Lumbar Spine
Together, they improve the security of the spine cord and roots. The dura is the most shallow however durable layer. The pia and arachnoid, together termed the leptomeninges, are frail. The spine, roots, and nerve rootlets are closely invested by the pia. The dura and arachnoid together form a loose sheath (termed dural/thecal sac) around these structures, separated from the canal walls by the epidural space.
The external surface is rough and mixes with loose connective tissue in the epidural space. The internal surface area, dealing with into the subdural space, is smooth and covered by a layer of mesothelium. Key Reference , the dural sac ends at the sacral canal, normally at S2-S3 (often S1). The dura continues caudally as a fibrous thread named the filum terminale externum or coccygeal ligament, which blends with the PLL over the coccyx.
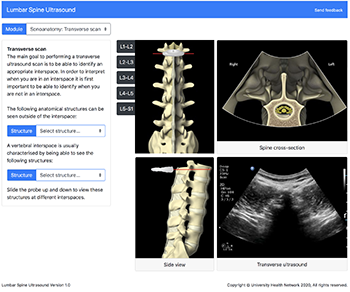
Lumbar Spine Pain: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments - Regenexx® at New Regeneration Orthopedics
The Ultimate Guide To Private Lumbar Spine Surgery - Manchester Centre for
Connective tissue insinuates the foramen anchor the dural sleeves so that they can protect the back nerve roots from being stretched throughout L-spine movements. In addition to these tetherings, the dura is attached in places to the PLL. Epidural area The epidural (peridural/extradural) space terminates inferiorly at the sacral hiatus, where it is sealed by the posterior sacrococcygeal ligaments.
The entire area is occupied by loose connective tissue with variable fat material, offering padding around the dural sac and spine and serving as a form to hold the thin internal vertebral plexus of veins open. The vertebral venous plexus is embedded in the epidural loose connective tissue, in some cases transferring large quantities of blood.
The Greatest Guide To Lumbar decompression surgery - NHS

A layer of mesothelium covers all leptomeningeal surfaces bathed by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The arachnoid mater lines the whole dural sac and extends into the dural sleeves. It likewise sends out trabeculae throughout the subarachnoid area to the pia, helping with CSF mixing. Along the posterior midline, the trabeculae form a distinct subarachnoid septum.
The pia mater supplies assistance for the vasculature and nerves in the subarachnoid space. It adheres thoroughly to the spine. The pia forms a separate sheath for each nerve rootlet and root as far laterally as the foramen, mixing with the epineurium. Caudally, the pia continues as the thin filum terminale internum.
